How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, whether for professional use or recreational purposes. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, covering everything from understanding fundamental components and regulations to mastering advanced flight techniques and troubleshooting common issues. We’ll explore the legal landscape, pre-flight checks, control mechanisms, and best practices for capturing stunning aerial footage, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies responsibly.
From understanding the basic flight controls to navigating complex flight modes and troubleshooting potential problems, this guide provides a structured approach to learning. We’ll cover essential safety procedures, regulatory compliance, and maintenance tips, empowering you to operate your drone confidently and safely. We’ll also examine various applications of drones, providing practical examples and insights into real-world scenarios.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Safe and legal drone operation requires understanding and adherence to regulations and safety protocols. This section details essential legal requirements and safety procedures for various locations and flight scenarios.
Drone Regulations in Different Locations

Drone regulations vary significantly depending on location. Urban areas often have stricter rules regarding airspace restrictions, flight altitudes, and permitted flight zones. National parks frequently prohibit drone flights altogether to protect wildlife and natural resources, or may require special permits. Before flying, always check local regulations and obtain necessary permissions. Websites of national aviation authorities (like the FAA in the US or the CAA in the UK) are excellent resources for finding this information.
Failing to comply can lead to fines or even legal action.
Drone Safety Procedures
Safety should be the paramount concern during every drone flight. This involves pre-flight checks, adherence to safe operating practices during the flight, and post-flight procedures to ensure the drone’s safe storage and maintenance.
- Before Flight: Conduct thorough pre-flight checks (detailed in the following section), check weather conditions, and ensure sufficient battery charge.
- During Flight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone at all times, avoid flying near people or obstacles, and be aware of surrounding airspace.
- After Flight: Power down the drone completely, inspect for damage, and store it in a safe, dry location.
Pre-Flight Drone Inspection Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist is crucial for preventing accidents. This checklist ensures all components are functioning correctly before commencing a flight.
- Inspect propellers for damage or cracks.
- Check motor functionality.
- Verify battery charge level and health.
- Ensure GPS signal is strong and accurate.
- Confirm camera and gimbal are functioning properly.
- Check all screws and fasteners are secure.
- Inspect the drone’s body for any damage.
Common Drone Accidents and Causes
Understanding common drone accidents and their causes can help pilots avoid similar situations.
| Accident Type | Cause | Prevention | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crash due to loss of signal | Interference, low battery, distance from controller | Maintain visual line of sight, fly within range | Emergency landing procedures |
| Collision with obstacle | Poor piloting skills, lack of awareness | Practice in open areas, plan flight path carefully | Reduce flight speed, use obstacle avoidance features |
| Battery failure | Low battery, faulty battery | Use high-quality batteries, monitor battery levels | Emergency landing procedures |
| Mechanical failure | Poor maintenance, damaged components | Regular maintenance, pre-flight checks | Immediate landing |
Understanding Drone Components and Functions
Understanding the function of each drone component is essential for safe and effective operation. This section describes the key components and their roles.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires knowledge of regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone and become a confident pilot. Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both personal safety and the safety of others.
Drone Component Functions
A typical drone consists of several key components working in unison.
- Propellers: Generate thrust for lift and maneuverability.
- Motors: Power the propellers.
- Battery: Provides power to the entire system.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, responsible for stability and flight control.
- Camera: Captures aerial imagery and video.
- GPS Module: Provides location data for navigation and stability (in GPS-enabled drones).
- Gimbal: Stabilizes the camera for smooth footage.
Drone Camera Types and Capabilities, How to operate a drone
Drones utilize various camera types with different capabilities, impacting image and video quality.
- Standard Cameras: Offer basic image and video capture.
- High-Resolution Cameras: Capture detailed images and videos.
- Thermal Cameras: Detect heat signatures for various applications.
- RGB Cameras: Capture true-color images.
The Flight Controller’s Role
The flight controller is the central processing unit of the drone, managing all flight aspects.
It receives input from various sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes, barometers, GPS), processes this data, and sends commands to the motors to maintain stability and execute pilot commands. Advanced flight controllers also incorporate features like obstacle avoidance and autonomous flight modes.
Drone Battery Types and Lifespans
Different drone batteries offer varying flight times and performance characteristics.
- Lithium Polymer (LiPo) Batteries: The most common type, offering high energy density but requiring careful handling.
- Lithium Ion (Li-ion) Batteries: Generally safer than LiPo batteries but may have lower energy density.
Battery lifespan is affected by factors like charge cycles, storage conditions, and usage patterns. Proper care and maintenance can extend the battery’s useful life.
Pre-Flight Preparations and Procedures
Thorough pre-flight preparations are crucial for a safe and successful drone flight. This section Artikels the necessary steps and checks.
Calibrating Drone Sensors and Compass
Calibration ensures accurate sensor readings, crucial for stable flight. This usually involves following the manufacturer’s instructions, often using a specific procedure within the drone’s control app or software. The process typically involves leveling the drone and performing a series of movements to allow the sensors to calibrate themselves.
Planning a Drone Flight Path
Planning the flight path beforehand is crucial for safety and efficiency. Consider factors such as airspace restrictions, obstacles, and the desired shots. Many drone apps allow for pre-programming flight paths, enabling autonomous flight within defined parameters. Always visualize the entire flight path before starting, considering potential hazards and emergency landing zones.
Pre-Flight Battery Checks and Charging
Battery health and charge are paramount. Check the battery level before each flight, ensuring sufficient charge for the planned flight duration. Use a reputable charger and follow manufacturer guidelines for charging procedures. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries, which can damage them.
- Check battery voltage.
- Inspect for any physical damage.
- Ensure proper connection to the drone.
Essential Accessories for Safe Drone Flight
Several accessories enhance safety and flight performance.
- Extra batteries
- Spare propellers
- Carrying case
- Calibration tools
- First-aid kit (for minor injuries)
Drone Flight Operation and Controls
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section covers basic maneuvers and flight modes.
Basic Flight Controls
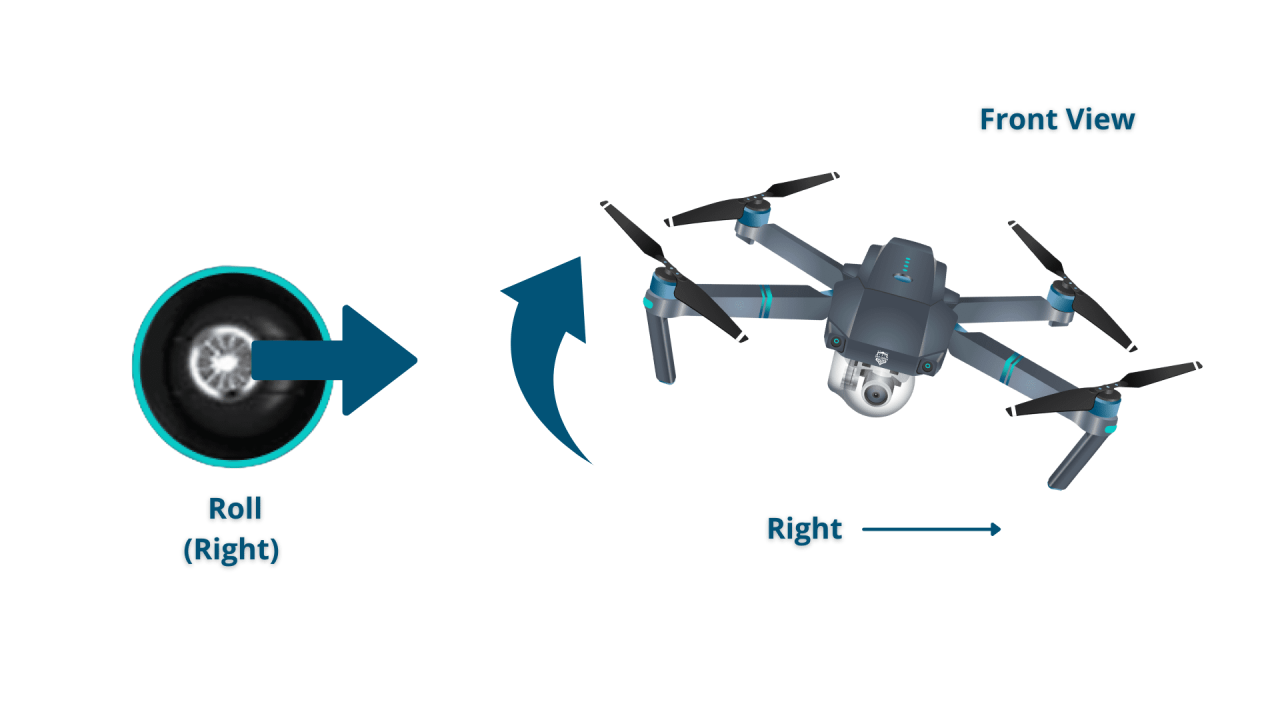
Most drones use a control system based on four axes: throttle (up/down), pitch (forward/backward), roll (left/right), and yaw (rotation).
- Throttle: Controls altitude.
- Pitch: Controls forward and backward movement.
- Roll: Controls left and right movement.
- Yaw: Controls rotation around the vertical axis.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
Safe takeoff and landing are critical for preventing accidents. Ensure the area is clear of obstacles and people. Start with a slow, controlled ascent and descent, maintaining visual contact with the drone. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area before attempting more complex flights.
Different Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and automation.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS for position holding and stability.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains orientation relative to the pilot, irrespective of GPS signal.
- Manual Mode: Offers direct control over all flight axes.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Mastering basic maneuvers is essential for safe and efficient drone operation.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude.
- Turning: Rotating the drone around its vertical axis.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
Advanced techniques enhance capabilities in challenging conditions and allow for creative aerial footage capture. This section covers advanced piloting and emergency procedures.
Flying in Challenging Conditions
Windy conditions and low light significantly impact drone stability and control. In windy conditions, reduce speed and maintain a stable heading. In low light, use extra caution, rely on GPS if available, and avoid pushing the drone’s limits. Always prioritize safety over ambitious shots.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Footage
High-quality aerial footage requires planning and skillful piloting. Consider factors like lighting, composition, and camera settings. Smooth movements and steady shots are key to professional-looking results. Experiment with different camera angles and perspectives to enhance visual appeal.
Common Drone Flight Errors and Avoidance
Understanding common errors helps prevent accidents.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning how to safely and effectively handle your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This site provides valuable information on various aspects of drone piloting, ensuring you’re well-prepared before taking to the skies.
Proper operation guarantees both successful flights and responsible drone usage.
- Loss of signal: Maintain visual line of sight, fly within range.
- Sudden gusts of wind: Fly in calm conditions or reduce speed.
- Battery depletion: Monitor battery levels and carry spares.
Emergency Procedures in Case of Drone Malfunction
In case of a malfunction, prioritize safety. If the drone becomes unresponsive, initiate an emergency landing procedure. This usually involves activating a return-to-home (RTH) function if available, or manually guiding the drone to a safe landing spot. If the drone is out of control, consider cutting power as a last resort.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan and performance of your drone. This section Artikels essential maintenance and troubleshooting steps.
Regular Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and prevents costly repairs.
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Check motor mounts for looseness.
- Clean the drone body and camera lens.
- Inspect battery connectors for corrosion.
- Update firmware regularly.
Cleaning and Storing a Drone
Proper cleaning and storage protect the drone from damage and extend its lifespan. Use a soft cloth to clean the drone body and lens, avoiding harsh chemicals. Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Troubleshooting common issues can save time and money.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Battery issues | Low charge, faulty battery, poor connection | Charge battery, replace faulty battery, check connections |
| Motor malfunctions | Damaged motor, loose connection | Replace motor, check connections |
| GPS problems | Weak signal, interference | Move to an open area, restart drone |
Preventative Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule helps prevent problems.
- Daily: Inspect propellers and body for damage.
- Weekly: Clean the drone and check battery health.
- Monthly: Perform a more thorough inspection of all components.
Illustrative Examples of Drone Operation
Real-world scenarios illustrate the practical application of drones across various fields. These examples demonstrate the versatility and capabilities of drone technology.
Aerial Photography Scenario

A photographer uses a drone to capture stunning aerial images of a cityscape at sunset. The flight is carefully planned to avoid obstacles and utilize optimal lighting conditions. The photographer uses a high-resolution camera and a gimbal to stabilize the shots, resulting in high-quality images showcasing the city’s beauty.
Drone Flight for Inspection Purposes
A construction company uses a drone equipped with a thermal camera to inspect a bridge for structural damage. The drone’s thermal imaging capabilities reveal areas of heat loss, indicating potential cracks or weaknesses in the bridge’s structure. This allows for early detection and preventative maintenance, ensuring public safety.
Drone Rescue Operation
A search and rescue team uses a drone equipped with a high-resolution camera and a thermal imaging sensor to locate a missing hiker in a mountainous region. The drone’s aerial view and thermal imaging capabilities allow the team to quickly locate the hiker, who was injured and stranded. The drone’s ability to access difficult terrain proves crucial in the successful rescue operation.
Drone Flight in a Challenging Environment
A wildlife researcher uses a drone to monitor a herd of elephants in a dense forest. The drone’s maneuverability allows it to navigate the dense vegetation and capture high-quality footage of the elephants’ behavior. The researcher uses specialized software to analyze the footage, gaining valuable insights into the elephants’ social dynamics and habitat use. The challenges involved include maintaining line of sight in the dense canopy and avoiding collisions with trees.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of drone technology, safety protocols, and operational procedures. By diligently following the Artikeld steps and prioritizing safety, you can confidently explore the exciting world of aerial flight, capturing breathtaking visuals and expanding your capabilities. Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to all applicable regulations.
FAQ Resource
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like automatic return-to-home.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies significantly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge.
What happens if I lose GPS signal while flying?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point. However, always maintain visual contact with your drone.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures.
